Egg Retrieval in IVF Treatment Procedure
Egg retrieval is a pivotal step in the IVF treatment procedure, where mature eggs are collected from a woman’s ovaries to be fertilized in a laboratory. This process is meticulously timed and carried out with precision to maximize the chances of successful fertilization and subsequent pregnancy. The procedure involves several preparatory steps, careful monitoring, and the actual retrieval process, all designed to ensure the highest quality eggs are obtained.
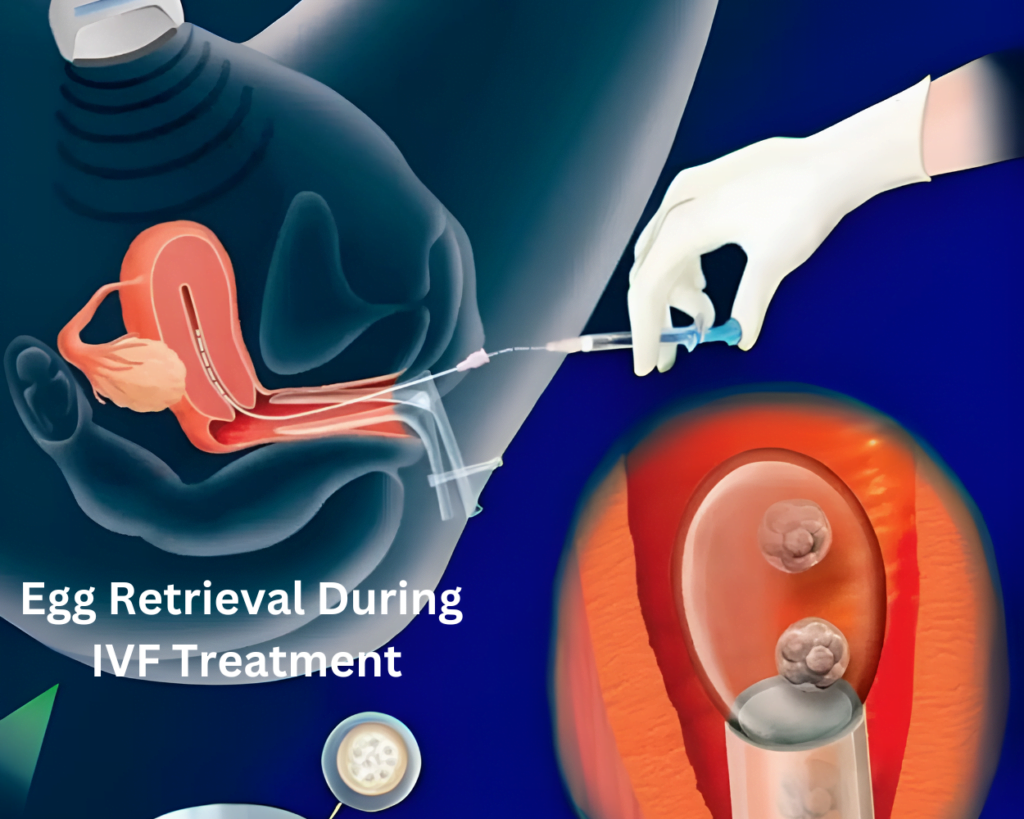
Egg Retrieval during IVF Treatment Procedure
During this procedure, an ultrasound probe is inserted into the vagina to locate the follicles. A needle is then carefully guided through the vaginal wall into the follicles. The eggs are aspirated from the follicles through the needle, which is attached to a suction device.
Key Components of Egg Retrieval
1. Preparation and Monitoring
- Hormonal Stimulation: Prior to egg retrieval, the ovaries are stimulated with hormonal medications (FSH and LH) to produce multiple follicles.
- Monitoring: Ultrasounds and blood tests are used to track the development of the follicles. This ensures that the eggs are maturing properly and helps in determining the optimal time for retrieval.
- Trigger Shot: About 36 hours before the retrieval, a trigger shot of hCG or a similar medication is administered to induce final maturation of the eggs.
2. The Egg Retrieval Procedure
- Sedation and Anesthesia: The procedure is typically performed under sedation or light anesthesia to ensure comfort.
- Transvaginal Ultrasound Aspiration: A thin needle is guided through the vaginal wall into the ovaries using ultrasound imaging. The needle aspirates the fluid from the follicles, collecting the eggs.
- Duration: The retrieval process generally takes around 20-30 minutes.
3. Post-Retrieval Care
- Recovery: Patients are monitored for a short period after the procedure to ensure there are no immediate complications. Mild cramping or spotting is common, and most patients can resume normal activities within a day or two.
- Egg Assessment: The retrieved eggs are evaluated for maturity and quality. Mature eggs are then prepared for fertilization in the laboratory.
Risks and Considerations
- Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS): A potential risk due to excessive response to hormonal stimulation, leading to swollen and painful ovaries.
- Infection and Bleeding: Though rare, there is a slight risk of infection or bleeding due to the needle aspiration.
- Emotional Stress: The process can be emotionally taxing, necessitating support and counseling.
Next Steps after Egg Retrieval
Post-retrieval, the eggs are fertilized with sperm in a laboratory setting. This marks the beginning of embryo development. The fertilized embryos are then cultured for a few days before being transferred to the uterus.
Emotional and Physical Considerations
- Counseling and Support: The egg retrieval process can be emotionally taxing. Counseling and support groups are beneficial for managing stress and emotional well-being throughout the IVF journey.
- Physical Well-being: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including proper nutrition and gentle exercise, can aid in recovery and overall well-being during the IVF process.
Conclusion
Egg retrieval is a critical component of the IVF treatment process, directly impacting the chances of achieving a successful pregnancy. Through careful preparation, precise execution, and post-procedure care, this step is designed to harvest the highest quality eggs. Understanding the intricacies of egg retrieval helps patients prepare for this crucial phase, ensuring they are well-informed and confident in their IVF journey.
For more detailed information on the steps following egg retrieval, such as embryo transfer and post-retrieval medication protocols, visit our Knowledgebase section.


